Radon is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and chemically inert radioactive gas. It is formed by the natural radioactive decay of uranium in rock, soil, and water. It can be found throughout North America. Testing for it is the only way of telling how much is present.
The EPA offers examples of where radon can enter a building structure:
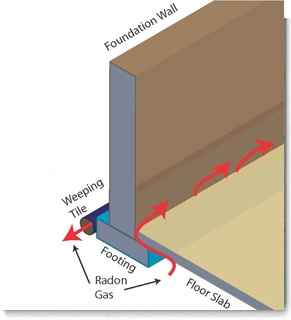
- Cracks in Solid Floors
- Construction Joints
- Cracks in Walls
- Gaps in Suspended Floors
- Gaps Around Service Pipes
- Cavities Inside Walls
- Water Supply


 icon and select "Add to Home Screen".
icon and select "Add to Home Screen".